IP address groups in NTA
NTA allows you to establish IP address groups for selective monitoring of custom categories or segments of your network.
With well-defined IP groups, you can better characterize and assess NetFlow data that you receive.
SolarWinds recommends creating IP Address Groups, for example by location, especially for the benefit of your first level support group, to quickly see IP Address ranges and makes things easier to manage.
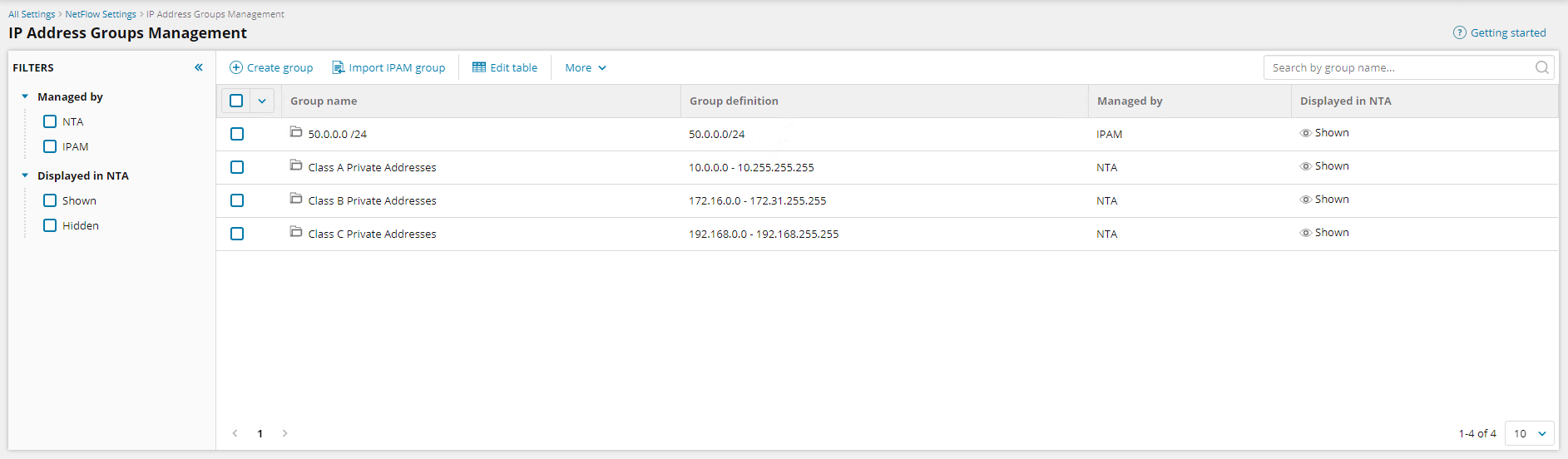
IP Address Groups Management page
You can manage your IP address groups through a completely reimplemented IP Address Groups Management page.
You can unify IP address groups with SolarWinds IPAM, define the IP Range with CIDR notation, filter IP address groups with predefined filters, or search IP address groups by their name and customize visible information. Changes on the IP Address Groups Management page are automatically confirmed, unlike in earlier versions of NTA where you had to click the Confirm button to apply the change.
All IP address groups features from previous versions of NTA are still available on the new management page, except for the explicit Printable version.
- Adding new IP address groups with ranges.
- Deleting IP address groups.
- Editing IP address groups and their ranges.
- Importing and exporting IP address groups from or to XML files.
- Enabling or disabling visibility of IP address groups in NTA widgets.
Access the IP Address Groups Management page
- In the SolarWinds Platform Web Console, click Settings > All Settings.
- Under Product Specific Settings, click NTA Settings.
- Under IP Address Groups, click Manage IP Address Groups.
Available actions
All IP address groups features from older versions of NTA are still available on the new management page, except for the explicit Printable version.
IP address group with ranges is created immediately after you click on the Create button. You can use CIDR notation to identify the IP address group range.
After selecting an IP address group, you can click Delete to remove IP address groups. You can bulk-delete by selecting multiple IP address groups. You must confirm the operation in another window what also provides and option for canceling.
After selecting an IP address group, you can edit the IP address groups. Changes are applied immediately after you click on Save. You can edit only one IP address group at a time. You cannot edit IP address groups managed by IPAM. You can use CIDR notation for IP ranges.
After selecting an IP address group, you can click Show for NTA to display IP address groups in widgets, or Hide in order to hide them. You can filter out the IP address groups that are either shown or hidden in the sidebar on the IP Address Groups Management page.

You can import IP address Groups managed by SolarWinds IPAM. For more information, see IP address groups unification with IPAM.
You can add IP address groups to existing groups or delete all existing groups by import new ones. If you choose to delete the existing IP address groups and replace them with imported ones, NTA check if the IP address groups are used by any NTA application. The operation is canceled if such an application is found. These application conflicts can be resolved automatically or manually. You can use CIDR notation when importing XML files. All IP address groups are imported as standard IP address groups managed by NTA, even when you export IP address groups previously imported from IPAM.


You can export the IP address groups in your SolarWinds Platform Web Console through the IP Address Groups Management page, clicking More > Export to file.

You can use standard features for the filtered list, such as filtering Shown or Hidden IP address groups or which product they are managed by, searching by IP address group name, or customizing the layout of the page and order of the columns.
Troubleshooting IP address groups
In NTA you can have IP address groups with overlapping ranges. Unlike IP address groups, applications cannot have groups with overlapped ranges in the same direction. If you have applications linked to a group (source, destination) and you edit or delete that group, you can create application collisions. These are overlaps in source or destination IP address groups. Application collisions are caused by editing or deleting an IP address group, or importing IP address groups from a file, deleting existing ones and replacing them with the new import. When a collision is detected, the operation is stopped and NTA will display a pop-up window with the collisions listed in a table, such as in the example below.

You can resolve the collision manually through the NTA Applications Management page or automatically by clicking Save & Delete in the pop-up window.
Application collisions are automatically resolved by deleting one of the applications in the collision. The applications with ![]() icon will be deleted. Applications with
icon will be deleted. Applications with ![]() will remain in the list.
will remain in the list.
Troubleshooting FAQs
Automatically resolving application conflicts during an IP address group synchronization can delete applications. If you do not want to delete any NTA applications, do not use IP address groups imported from IPAM for application definition.
When you update IP ranges including IP segments, historical data are not valid and widgets can show mismatched data. This situation is temporary. Changing an IP group range in IPAM can cause this behavior, too.
It is possible that someone else is editing IP address groups at the same time, or IP address group synchronization is running on the background. In such a case, conflicts are automatically resolved, but the other updates make change in IP address groups causing new conflicts. You have to resolve the conflicts again. This situation should be rare.
This is the expected behavior. All IP Groups are imported as IP Groups managed by NTA. Also, there is no possibility of how to "link" those IP Groups to existing IPAM groups. User has to delete those groups and import them again from IPAM.
SolarWinds cannot guarantee that while the applications are still managed by IPAM. In the current implementation, you cannot have synchronized groups managed by IPAM used in applications without the risk of deleting the applications during synchronization with IPAM. You can use IP groups managed by IPAM without this risk if you don't use them as a source or destination IP address group for applications. The only safe workaround is to:
- Import IP address groups from IPAM as IP address groups managed by IPAM.
- Export all IP address groups.
- Import IP address groups as IP address groups managed by NTA, deleting the existing groups.
The synchronization will not delete any application because there is no group to synchronize. But changes in IPAM will not be propagated into NTA anymore.
Go to the NTA Application Management page. Find the applications listed in the Application Conflicts window and edit them to remove conflicts. The specific resolution depends on your needs and possibilities you have to modify your applications.
Applications are usually conflicted in the following properties:
- Protocol (TCP, UDP, or both)
- Port number or port numbers for multiport applications,
- Source and destination IP address group.
The following options are available for resolving such conflicts:
- Delete one of the conflicting applications. This is how auto-resolve works, but you have a chance to choose the application to be deleted.
- Remove overlapping IP address group or IP address groups from the application. This IP address group still exists, but NTA will not use it as a source or destination IP address group of the application. You can create new IP address groups without overlaps by removing overlapping parts of the range and use these groups for edited applications. These steps can create a new application collision, but the Application Management page will inform you about it. This step can be used if you cannot edit the range of the original IP Group used for the application.
- Manually edit ranges of the colliding IP address groups to eliminate overlaps.
- If you have an Application with only one IP address group (source or destination, not both) in conflict, you can resolve the conflict by configuring the second IP address group, making this application more specific. This application will not be in collision anymore because more specific applications are preferred in processing.
- For multiport applications, you can remove the overlapping port.
- For applications with both protocols, you can set the protocol to TCP or UDP, so the protocol does not overlap with other applications.
