Populate the default credential ring
A credential ring maps user credentials to managed resources (such as computers and servers). Patch Manager uses a default credential ring to identify which credentials to pull from the database before performing tasks on the managed computers in your corporate enterprise. This role-based method enables the application to know which credentials to use to perform a specific task on a specific managed system.
If Patch Manager does not have the proper credentials to log in to the managed systems, the application generates Access Denied errors during a software update.
When you install Patch Manager, the application includes a default credential ring to store the administrator credentials required to access each system you inventory and manage. Populate the default credential ring with the administrator username and password of the inventoried systems to enable WSUS to log in and install software updates. For example, you can populate the credential ring with the administrator credentials required to access all systems in the Finance department.
After you configure the group policy to enable third-party updates, Patch Manager uses the administrator credentials in the default credential ring to update the group policy on all systems in the targeted department or workgroup.
To populate the default credential ring with the admin credentials:
- Add the administrator credentials to the credential ring.
- Assign the administrator credentials to the targeted resource.
- Use an organizational unit for the ring credential.
Add the administrator credentials to the credential ring
Add the administrator credentials to the Credentials tab in Security and User Management. These credentials are required for Patch Manager to log in and perform software updates on all systems that receive software updates from the WSUS server. When you are finished, configure the administrator credentials to the credential ring.
The following example shows you how to add a credential to the default credential ring.
- Locate and record the administrator credentials for the targeted systems in the department or workgroup. For example, record the administrator credentials used to access the computers and servers in the Finance department.
-
In the Patch Manager menu, maximize Patch Manager System Configuration and select Security and User Management.

-
Click the Credentials tab.

- Click Add Credential in the Actions menu.
-
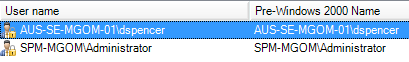
Enter the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the administrator who can log in to all computers in the targeted workgroup or department.
SolarWinds recommends entering the user name in the
DOMAIN\usernameformat. For example, if the targeted systems are located in theAUS-SE-MGOM-01domain anddspenceris the domain administrator, enterAUS-SE-MGOM-01\dspencerin the User Name field.
- Enter and confirm a password, and click Save.
- Repeat step 3 through step 6 to add additional administrator credentials for additional departments or workgroups that receive software updates from the WSUS server.
Assign the credentials to the targeted resource
Assign the credentials in the credential ring to the targeted resource. This process allows Patch Manager to log in to a managed system based on the credential rule.
The following procedure explains how to assign a credential rule to the Computers resource.
-
Click the Credential Rings tab.

-
Double-click <Default> to open the Credential and Credential Rings Rules wizard.

-
Accept the default credential ring.

-
Click the User Name drop-down menu, select an existing credential, and click Add.
To add a credential, complete the User Name and password fields, and click Add.

-
Review the credentials, add additional credentials as needed, and click Next.

- Map the credentials to the targeted resource.
- Click Add Rule.
Select the type of rule you want to add.
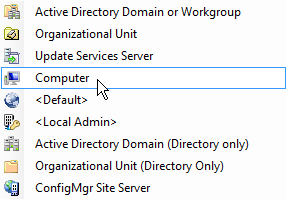
In the left pane of the Select Computer window, browse the left pane until the resource you want to add is in the upper right pane.
- In the center window, select the resources you want to include in the credential rule, and then click Add selected.
- Repeat these steps for each resource you want to add.
- Click OK.
On the Select User for Credential Rule window, select the credential you want to map to the resources, and then click OK.
Click OK.
The credentials are assigned to the targeted resources.
In this example, when Patch Manager logs in to client systems in the
se-aus-mgom-03domain to download a patch, the application uses theAUS-SE-MGOM-01\dspencercredentials to log in to the systems. Any resource (such as Active Directory Domains and Workgroups) that is not assigned to a rule defaults to theUnmatched resourcescredentials.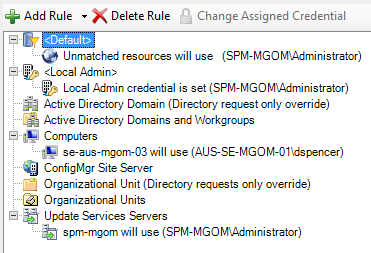
Ensure that the
Default>Unmatched resourcescredential rule is assigned to a system administrator with administrator rights to the managed systems and the environment. If a credential rule (for example, Computers or Update Services Servers) is not assigned to a system administrator with the proper credentials, the rule defaults toUnmatched resources.If you push a task to the managed computers and the rule defaults to
Unmatched resourceswithout the proper credentials, you can receive Access Denied errors when you push a task to the managed computers.
-
Click Finish
The credentials are assigned to the targeted resource. When Patch Manager connects to the targeted resources, it uses the credentials you assigned to the credential ring to log in to the managed systems as the assigned administrator and install the software updates.
Use an organization unit rule for the ring credential
The organizational unit (OU) rule is used when a selected computer is scoped to the OU (or computers and groups within the OU).
When you use an organizational unit (OU) rule for credential matching, ensure that the computers are added to the OU in Active Directory. In the following example, SPMOU is the OU group.

When you add the domain in the Patch Manager Console and scope the domain and corresponding OU of the domain in the console, the computers should be listed, as shown below.

If you scope the computer through another means, the OU rule will not be considered.
For example, if you scope to a computer using a Patch Manager Computer group, the scope will always be "computer" and the scope will only check the computer rules and disregard the OU rules.
When you perform update management or other tasks on a computer using the OU rule, select your target scope using the OU of the domain in Patch Manager.

When you complete the procedure, the computer is added to the OU group.

