IP address conflicts
IPAM actively scans your network and if any duplicate static IP assignments or duplicate IP provisioning from a DHCP server are detected an event is triggered in the IP Address Conflicts widget on the IP Address Summary page. IPAM also detects if there is more than one MAC address using the same IP address within the same network. IPAM looks for differences in MAC addresses, from two distinct simultaneous scans for a single IP address, within a subnet.
The event information displays the IP address, conflict type, subnet, and MAC addresses that are in conflict, as shown below.
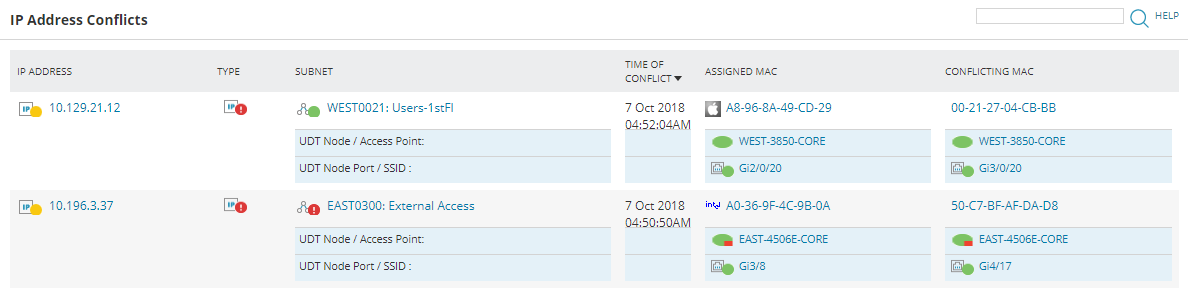
Here, two devices on the WEST0021 subnet (and two on the EAST0300 subnet) are in conflict.
Move the cursor over the Type icon to show the conflict type (for example, Scope overlap, Dynamic + Static)
If UDT is installed additional information is displayed, showing node and node port details.
Click on an IP address to show the IPAM IP Address Details page. The IP Address Conflict Details widget shown below is displayed.
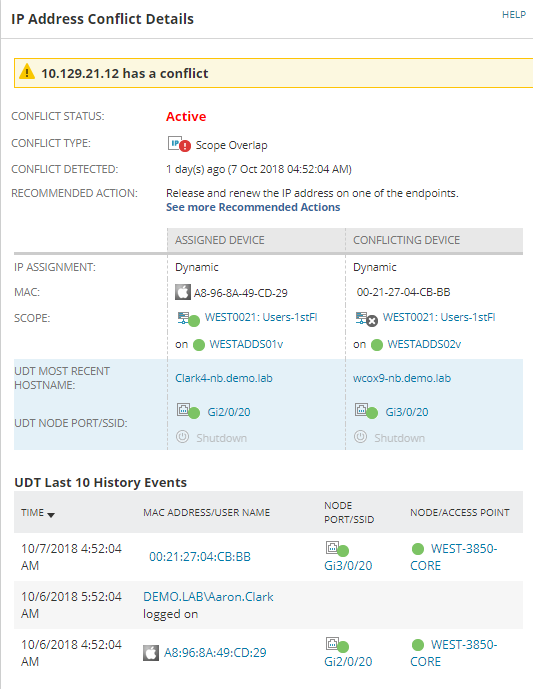
Recommended action is displayed. Click See more Recommended Actions to display further actions.
See the table below for further information about the different kinds of IP Address conflict and how to remedy these.
If UDT is installed, this widget will show the last ten events for this IP address enabling you to track down the cause and responsibility for the conflict.
IP address conflict scenarios
IPAM automatically detects IP conflicts by scanning servers and devices, and alerts you when conflicts are found. IPAM alerts for the following IP address conflict scenarios.
During subnet scans, MAC addresses obtained from SNMP, SNMP neighbor, and IPAM reservations are called Static entries and those obtained from DHCP servers are called Dynamic entries.
The different kinds of IP address conflicts are:
| Type | Description | Remedy | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Static and Static |
SNMP versus SNMP Neighbor |
There is a conflict in the MAC addresses retrieved from the ARP table of the configured device and from the SNMP OIDs during the subnet scan for an IP address. |
|
| IPAM reservation versus SNMP/SNMP neighbor | There are situations where you reserve an IP address under a subnet in IPAM that contains a MAC address for an internal reference. This type of conflict occurs when there is a difference in MAC addressees from either SNMP OIDs, or neighbor devices with reserved MAC addresses in IPAM. | ||
|
Static and Dynamic |
SNMP versus DHCP | There is a difference in the MAC addresses fetched from an SNMP OID and DHCP leases from a DHCP server, for an IP address during a subnet scan. |
|
|
SNMP Neighbor versus DHCP |
There is a difference in the MAC addresses retrieved from the ARP table of the configured device and from DHCP leases from the DHCP server. | ||
| IPAM reservation versus DHCP | There are situations where you reserve an IP address under a subnet in IPAM that contains a MAC address for an internal reference. This type of conflict occurs when there is a difference in MAC addressees from DHCP leases with reserved MAC addresses in IPAM. | ||
|
Dynamic and Dynamic |
DHCP versus DHCP | A range of IP addresses within a subnet may be managed by two DHCP servers. This conflict occurs when there is a difference in MAC addresses retrieved from the two DHCP servers' lease information. |
|
|
|
A range of IP addresses within a subnet may be managed by two DHCP servers. There are cases when a part of an IP address range under one DHCP server is managed by another DHCP server. In both instances, there is an overlap in scopes between two DHCP servers. This is considered a conflict. | ||
