Charts
Creating a New Chart
When you start with a new dashboards you'll see a placeholder for a chart with a large plus in it. To add charts to existing dashboard just click on the plus button in the menu bar.
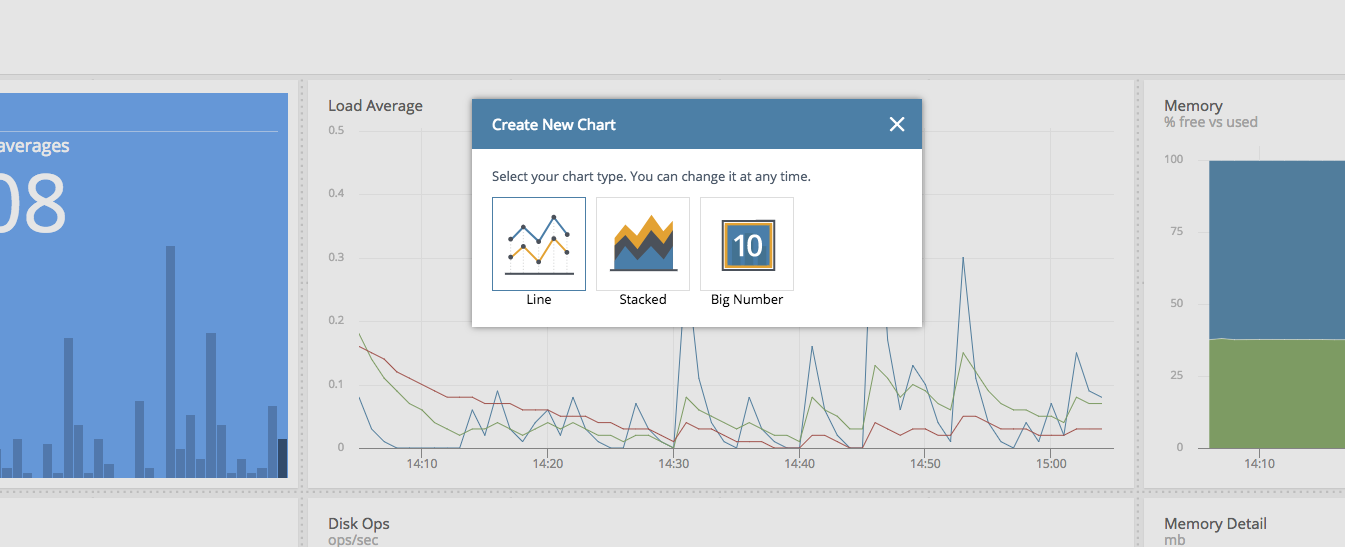
As a next step you choose the chart type. If you can't decide don't worry, you can change it later.
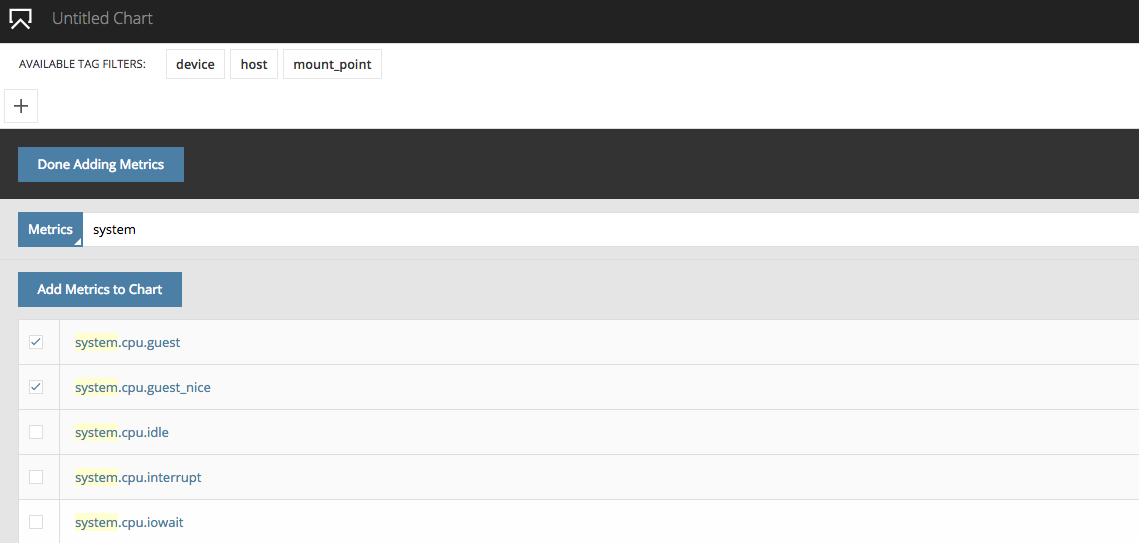
After choosing the type of chart you'd like to create the chart editor will slide up from the bottom of the page. The chart editor shows you a list of the metrics you're currently emitting to our API. You can narrow down the list by typing a pattern into the search box. As soon as you start typing the list is filtered.
Adding Metrics to a Chart
Add one or more metrics to the chart by checking them, and clicking the Add Metrics to Chart button.
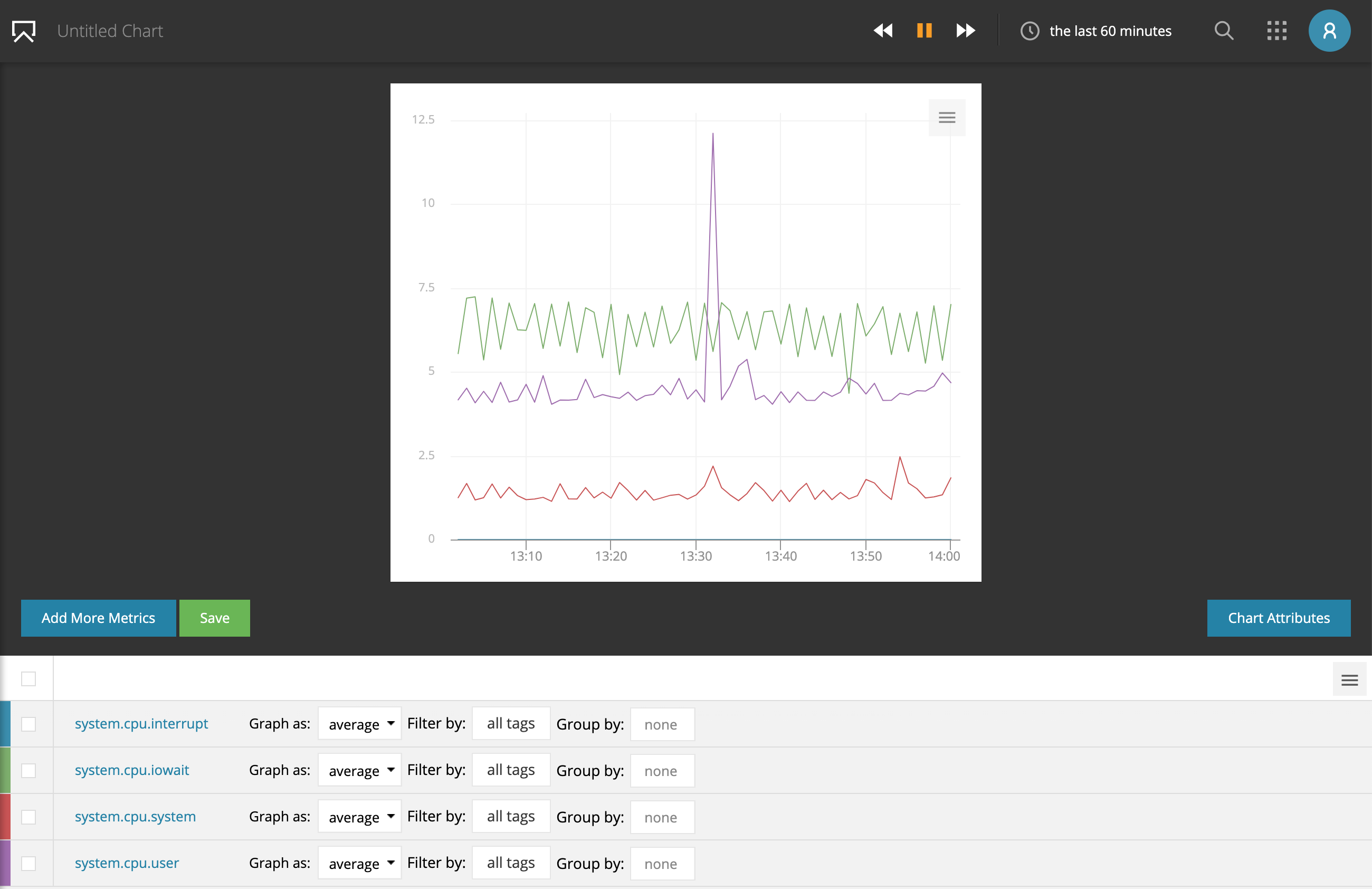
After adding metrics you can see a preview of your chart.
Moving the Chart
Hover over the top of a chart and you will see three dots appear. Simply grab the dots and move the chart around.
Chart Types
We currenlty offer three different visualization types: line charts, stacked area charts and big number charts.
Line Chart
A Line Chart is the go to chart type when representing time series data. AppOptics has a default color palette it assigns to series when rendering a chart. If you have a number of series on a chart, colors will be assigned randomly. If you have multiple metrics that each have several time series, the searies for each metric are all assigned the same color but with a different hue to distinguish them as a group. To learn more about colors please read the How to change the colors on a metric article.
Stacked Area Chart
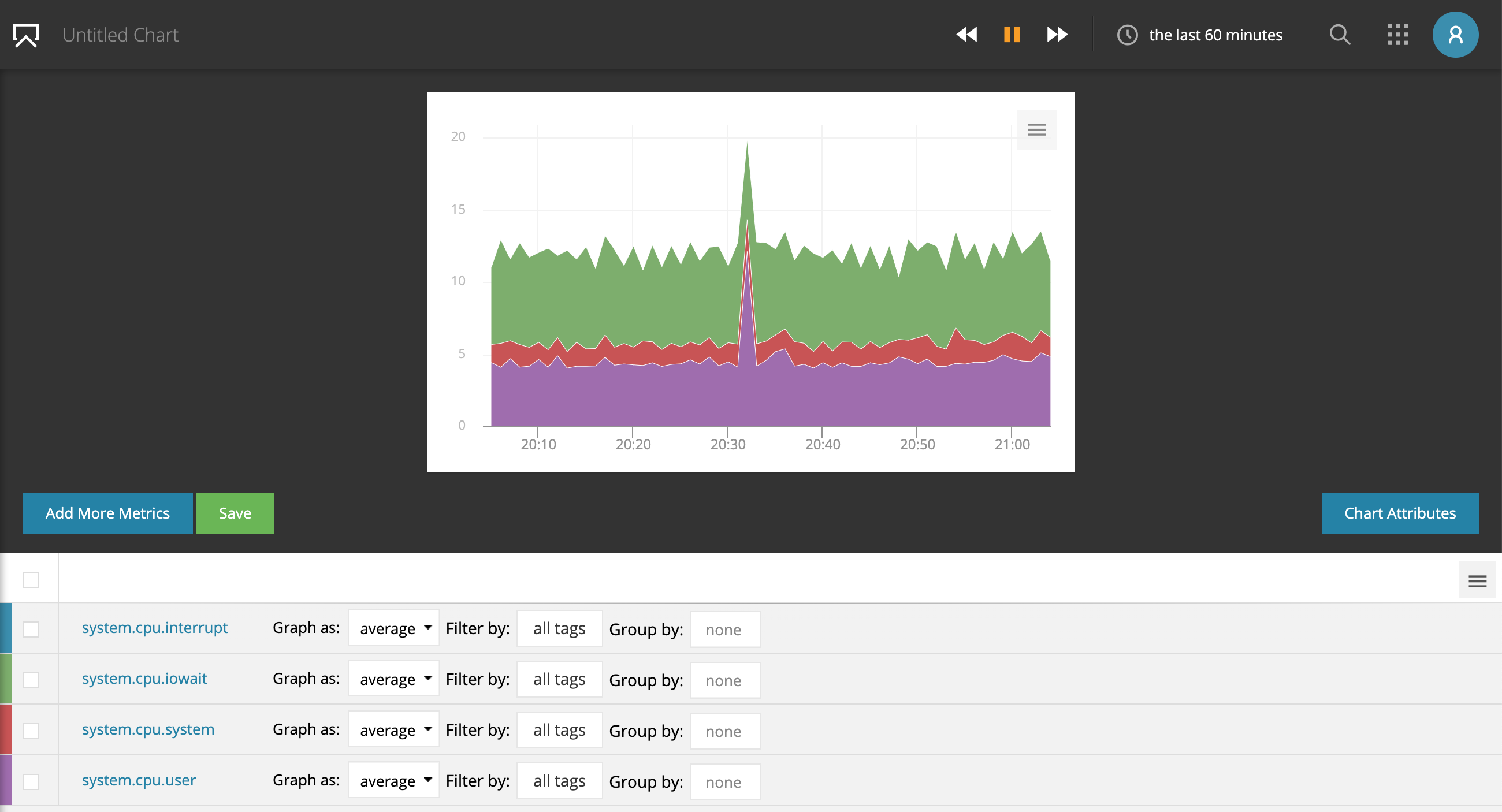
When you create a Stacked Area Chart, and add a single metric it will show as an area chart. If you add multiple metrics they will stack. You can also add a single metric with multiple streams, then group by a tag, and each data stream for that metric will be stacked.
If you add two metrics that each have multiple streams we will try to use shades of the same color to differentiate the metrics - that only works well with reasonable amounts of streams though.
If you add a series to an existing chart, the series will be added at the bottom of the chart.
Big Number Display
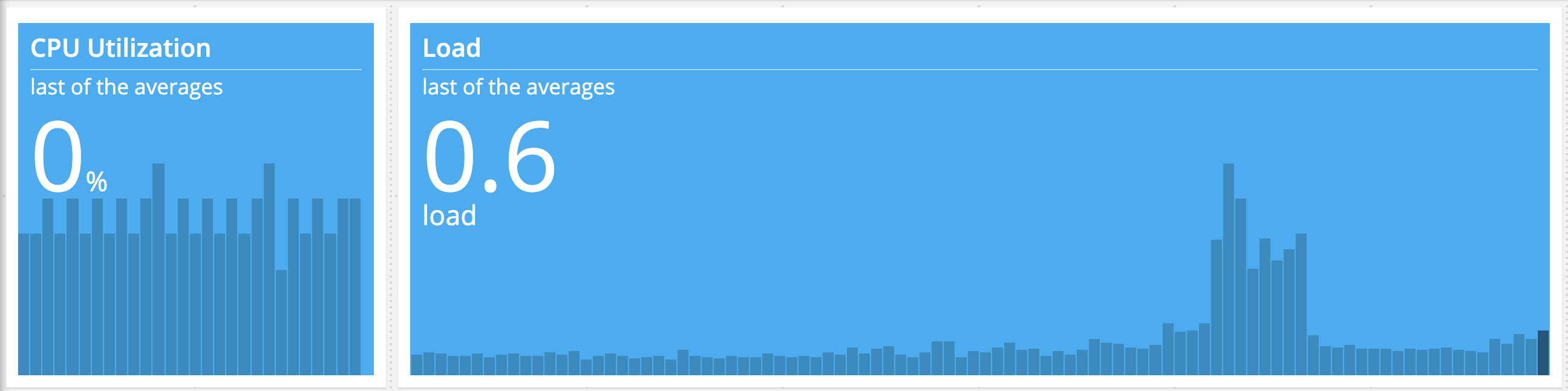
The Big Number chart allows you to focus on your most important numbers while also providing trending information at a glance. By design Big Number is a single metric chart. It can also be paired with our composite metrics to easily display derived values.
The number displayed by Big Number can be one of two things:
- the last value of the metric (last mode) or
- an aggregate of the data points in the current time window (reduce mode).
When your Big Number is in reduce mode, we use the stream's summarization function (sum, average, min, max) to determine how to perform the aggregation. If the metric is a composite, you can tell us via the UI what function you prefer.
To increase the insight into your data, the background of Big Number shows you the trend of your metric over time as a bar graph. This helps you to put the number into context.
Big Number Thresholds
With Big Number thresholds you can change the background color of the Big Number display based on thresholds. You can chose from two threshold types: critical and warning. Each type can be customized to trigger when the value goes either above or below a numerical threshold. Chart Thresholds update in real time.
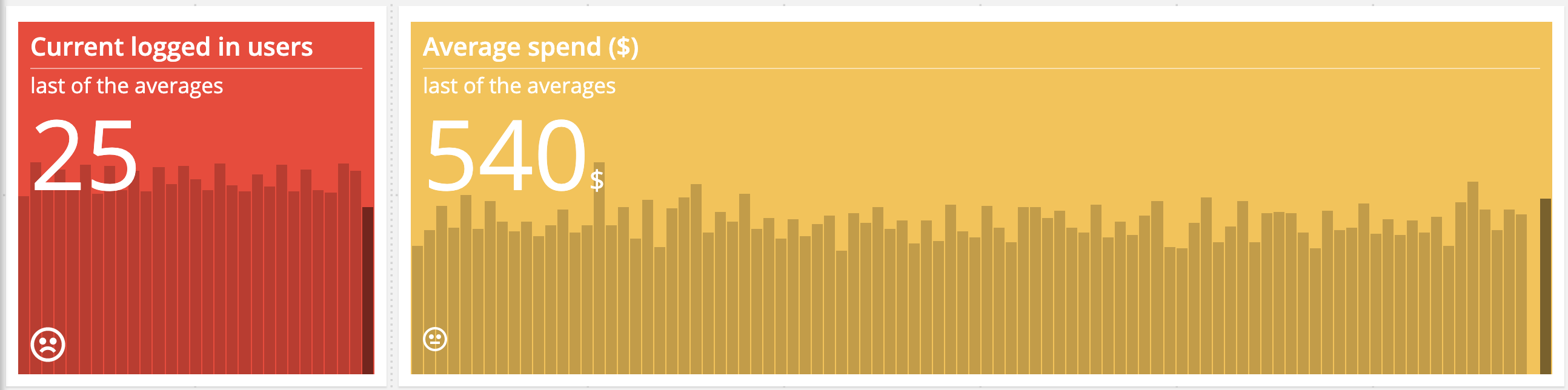
Big Number Decimal Notation
With the decimal notation option you can define a fixed number of decimals. This is useful for metrics such as currency (lock to 2 decimals), or availability metrics (e.g. five nines: 99.999%).
Composing Data Streams
Assuming data exists for the current time-interval displayed by the chart, you will typically see one line per metric. Even if you are submitting the CPU Utilization metric for 100 servers, you will only see a single line because of how the data streams are summarized, filtered, and grouped, or as how we call it: because of the stream composition. If graph as is set to average it means that every data point is computed by averaging over each data stream.
To see one line per value for a particular tag, set the grouping function (group by) to the tag you wish to see the breakout of. Using the CPU Utilization example from above, if you check the group by check box for the hostname tag, you will see 100 lines, one for each host.
Summarizing
Graph as defines how your metric data is summarized across data streams as defined by the tag set.
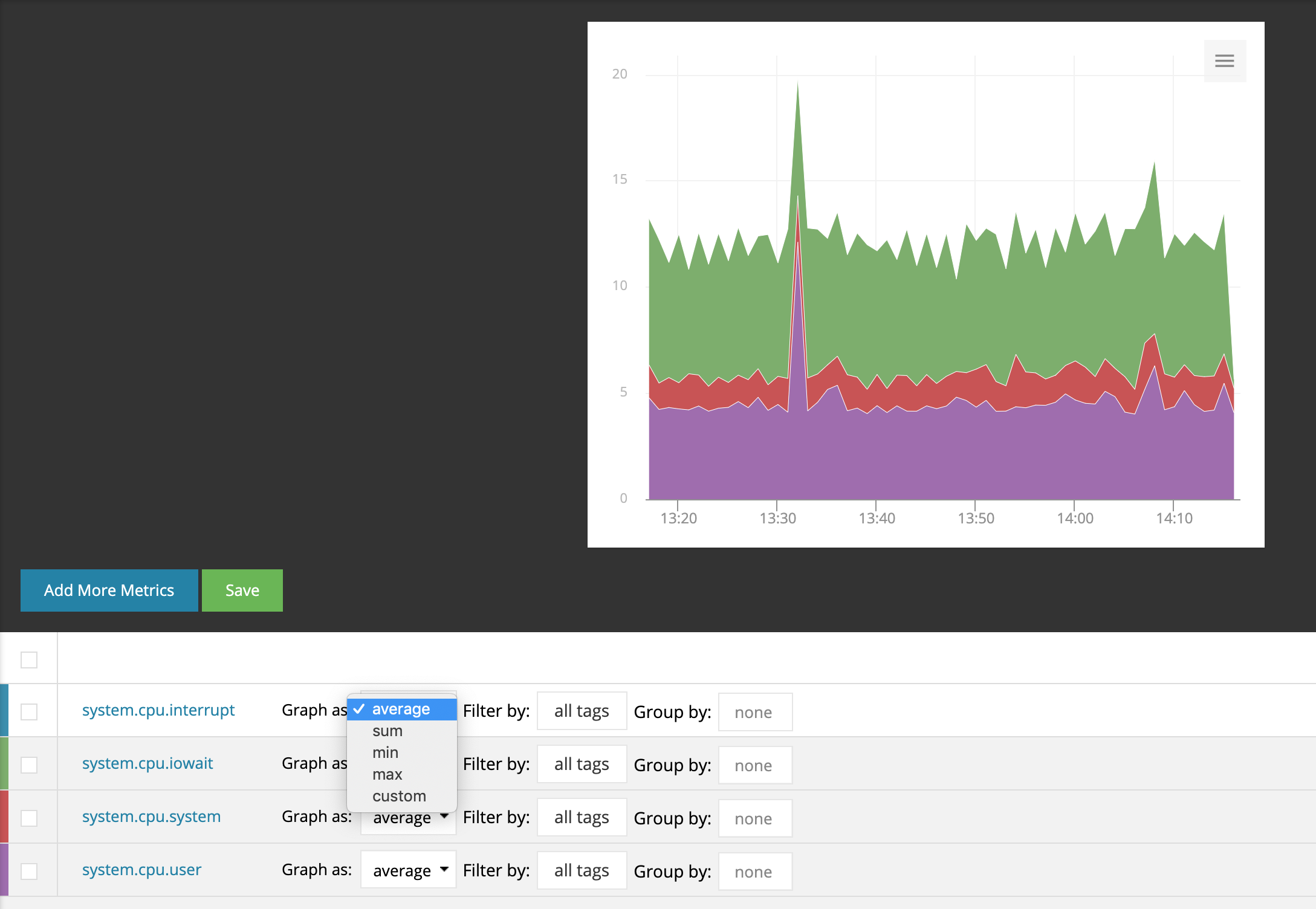
The available options for summarizing across data streams are:
- average
- sum
- min
- max
- custom (opens option to summarize across time)
If you chose the custom option you will be presented with a second field to select how your metric data is summarized across Time.
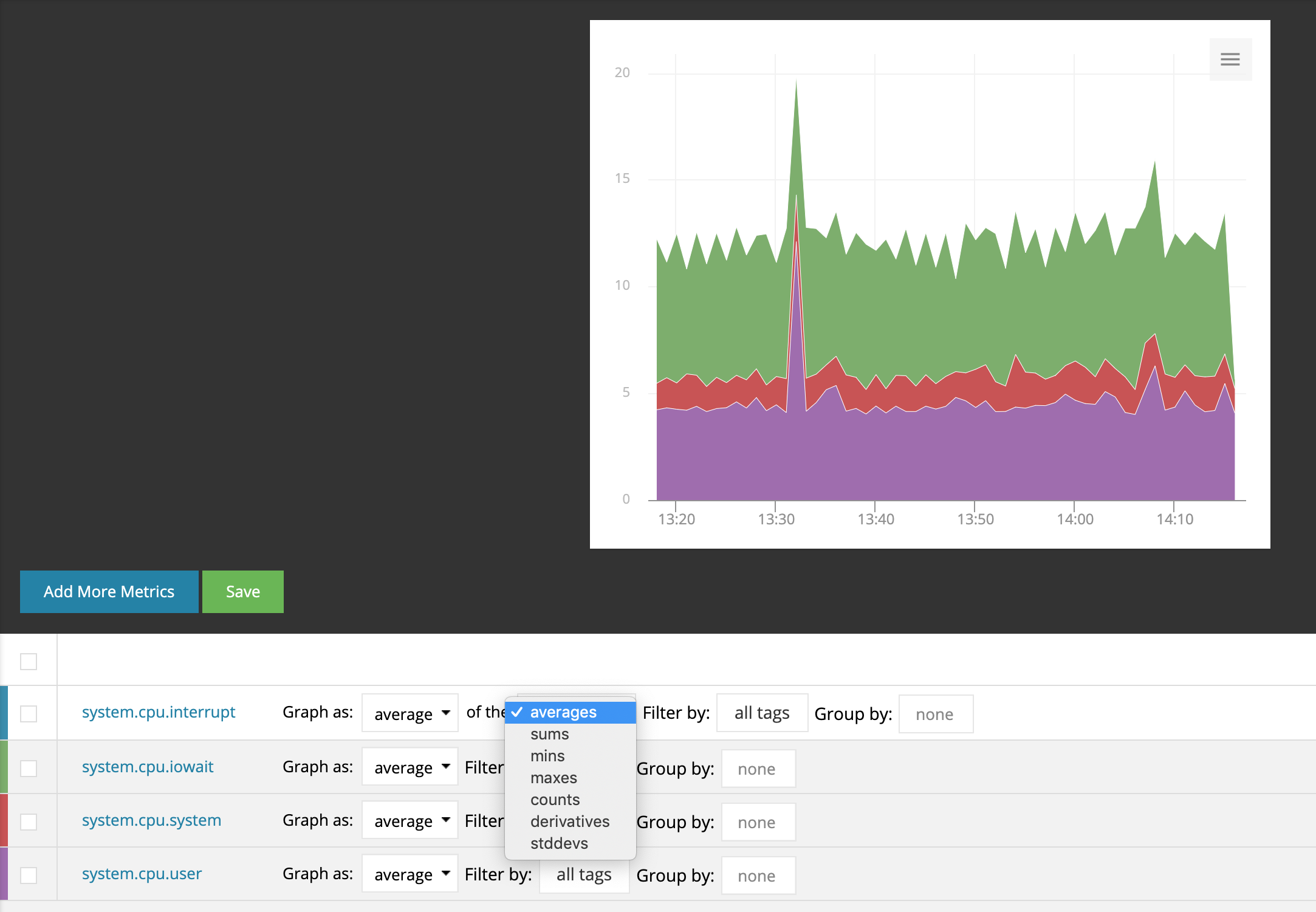
For example, Max of the Maxes will draw a single line for all streams in a specified tag set consisting of the maximum value across all data streams that each return the maximum value in each time interval. This setting overrides the aggregation function defined in the Metric Types. Options for how you summarize data streams over time (the x-axis) are:
- averages
- sums
- mins
- maxes
- counts (this is the count of measurements in the period)
- derivatives
- stddevs (standard deviations)
Filtering
The where paramater allows you to filter the data streams by a tag.
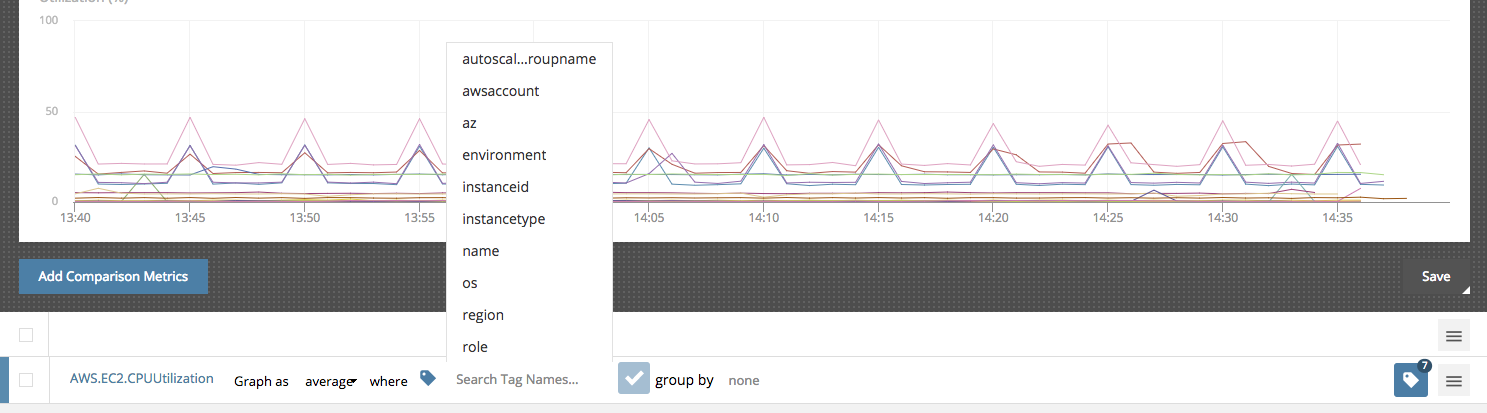
As an example, if you only want to chart the AWS.EC2.CPUUtilization of your testing environment, you can filter the data streams by using the environment tag and selecting testing.

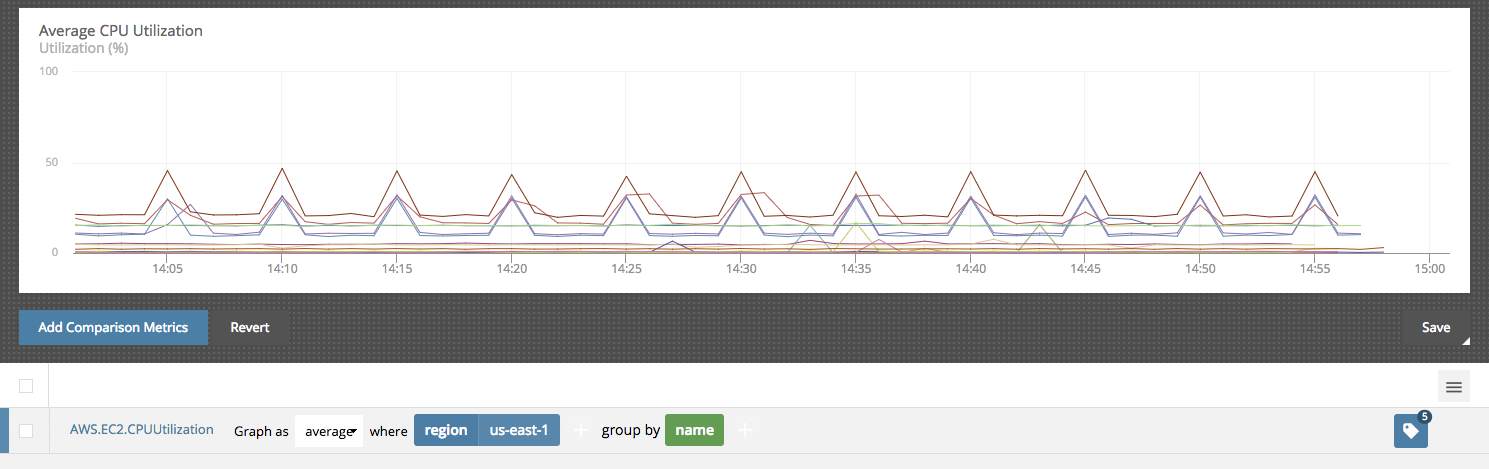
Grouping
The group by parameter allows you to group data streams by unique tag values. In the following example the data streams are filtered by the region tag to only show us-east-1 data and then grouped by the name tag. This results in one line for each AWS.EC2.CPUUtilization tagged with a name.
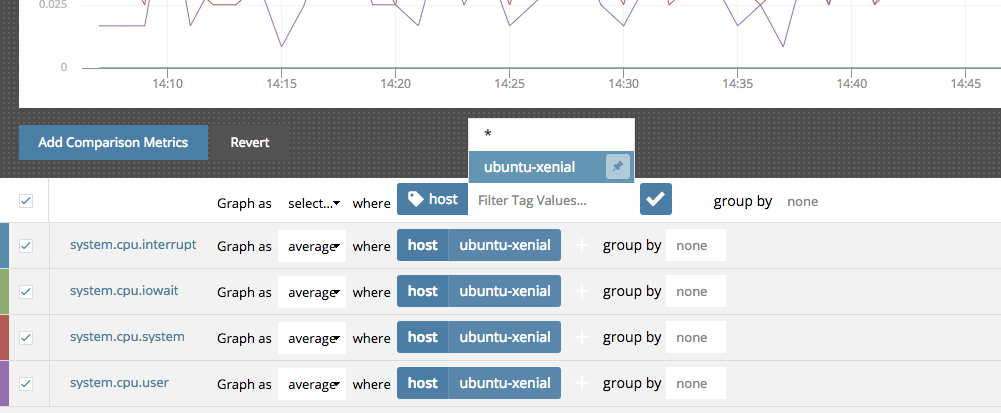
Mass Editing Filters and Tag Sets
You edit the stream composition for each metric individually or by checking multiple metrics and using the mass edit options.
Stream Attributes
Each stream on a chart has a number of attributes you can modify such as the color or whether to use a separate y-axis. To view and modify these attributes, hover over the data stream and a hamburger menu will appear on the far right of the row.
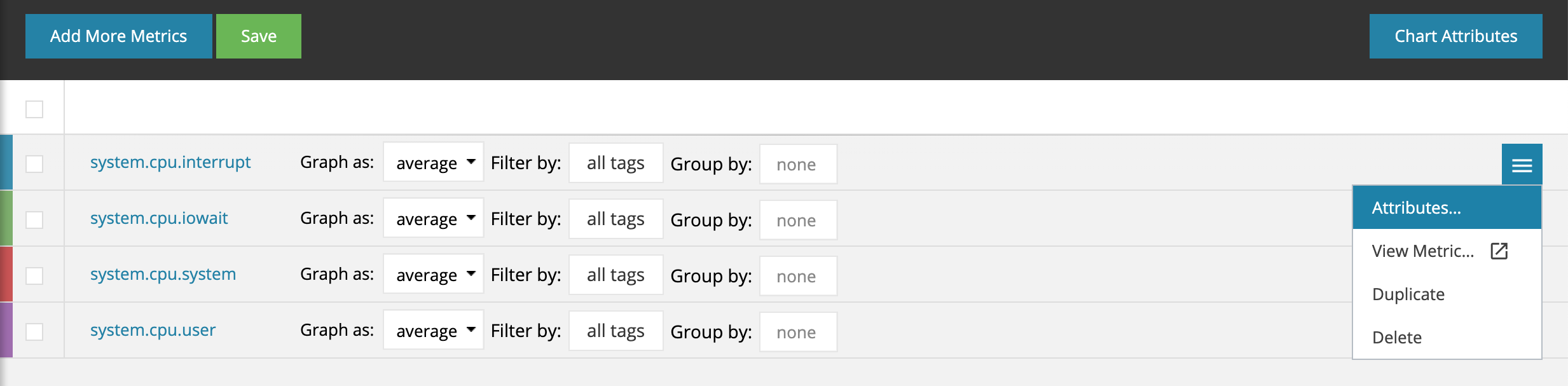
Clicking on "Attributes" in the pull-down menu will bring up a modal:
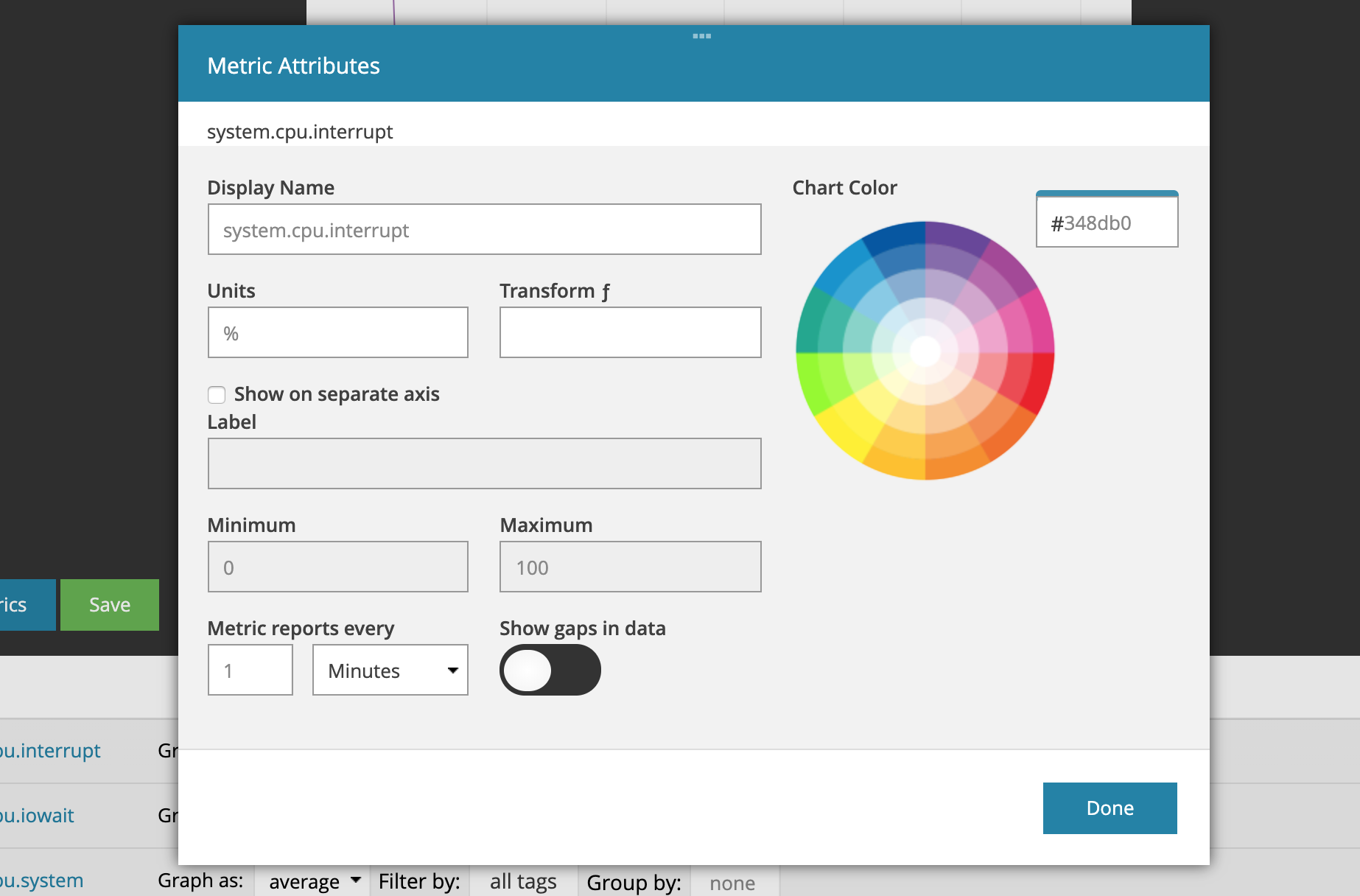
The attributes you can edit are:
- Display Name: Metric name displayed by the tooltip.
- Color: Set the color of your metric either via hex code or the color picker (read more here).
- Units: Units label displayed by the tooltip.
- Transform: Apply a simple formula to the data to, for example, convert between units like Fahrenheit to Celsius ((x-32)/1.8), or compute rates (x/p). Permitted variables are x (data point) and p (period). Read more about display transforms.
- Show on Separate Axis: Check this to set a custom Y-axis label
for this metric.
- Label: Custom name for the y-axis. Every metric in a chart that shares the same y-axis name, shares the same y-axis. Conversely, each metric with a Unique y-axis name creates and uses it’s own y-axis in the chart.
- Minimum: Set the minimum value of the y-axis, e.g. if you only expect positive values you can set this to 0.
- Maximum: Set the maximum value of the y-axis, e.g. if you are tracking a percentage you can set this to 100.
- Metric reports every: Interval at which you are sending us data (otherwise knows as the period). We use this setting along with the Reports Infrequently setting to properly handle gap-detection for your data. If the period is set, gaps will show for periods where no data is received. If it is not set, data points will be connected. Read more in the API docs.
- Show gaps in data: Some metrics are reported opportunistically. For example, every n seconds a measurement is sent only if there is new data. This results in a sparsely populated series. We use this setting in combination with the Period to correctly handle Gap-Detection.
Understanding the Y-axis label, Period, and Reports Infrequently settings are key to your happiness as a customer using AppOptics. We highly encourage you to read up on these settings and experiment with them until they are friendly and familiar.
Chart Menu
In the top right hand corner of the chart there's a menu button that gives you access to chart specific functions. Here you can choose to edit or delete the chart, change the chart type (for example from line chart to stacked chart), take a snapshot, and access the chart attributes.
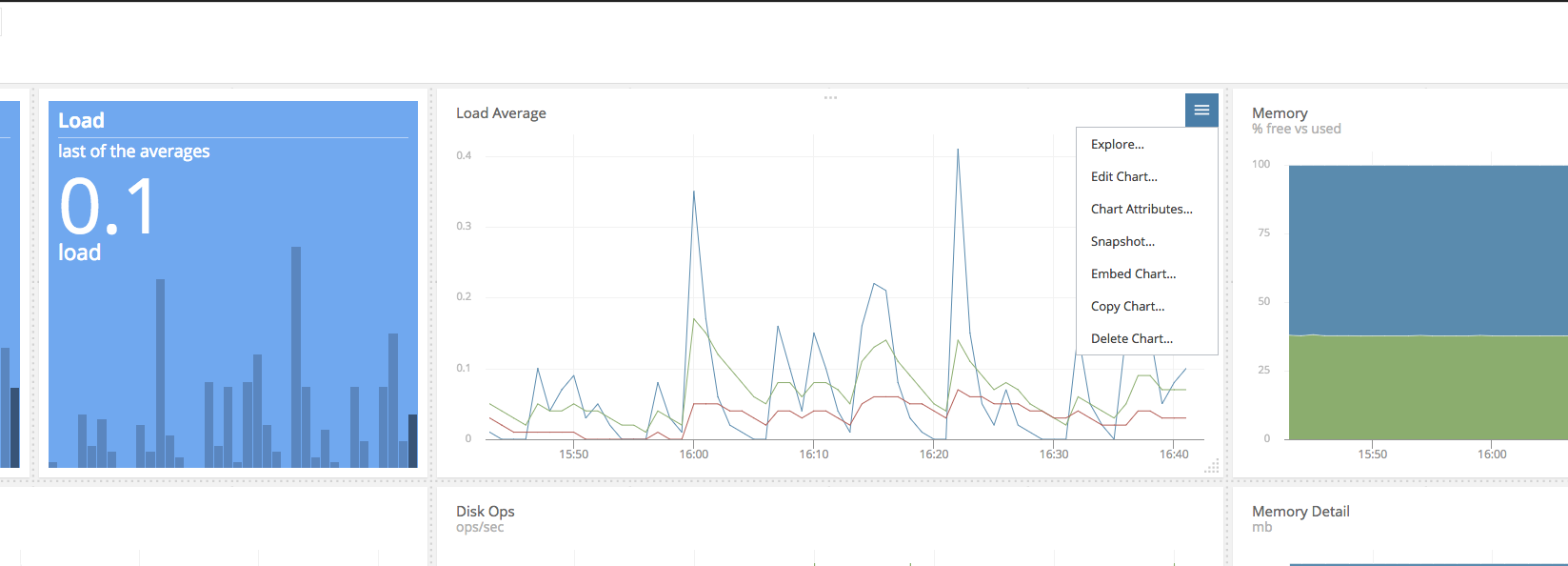
Explore View
The Explore view is what we call the fire-fighting view. You can either get to it via the menu option or by simply double clicking on a chart.
This view allows you to investigate details of the chart: look at and modify the stream composition, and stream attributes, add other metrics and / or annotations to check for correlations, all the while keeping your original configuration in tact. If you like the changes you make and want to save them, you can either overwrite the existing chart or save it as a new one.
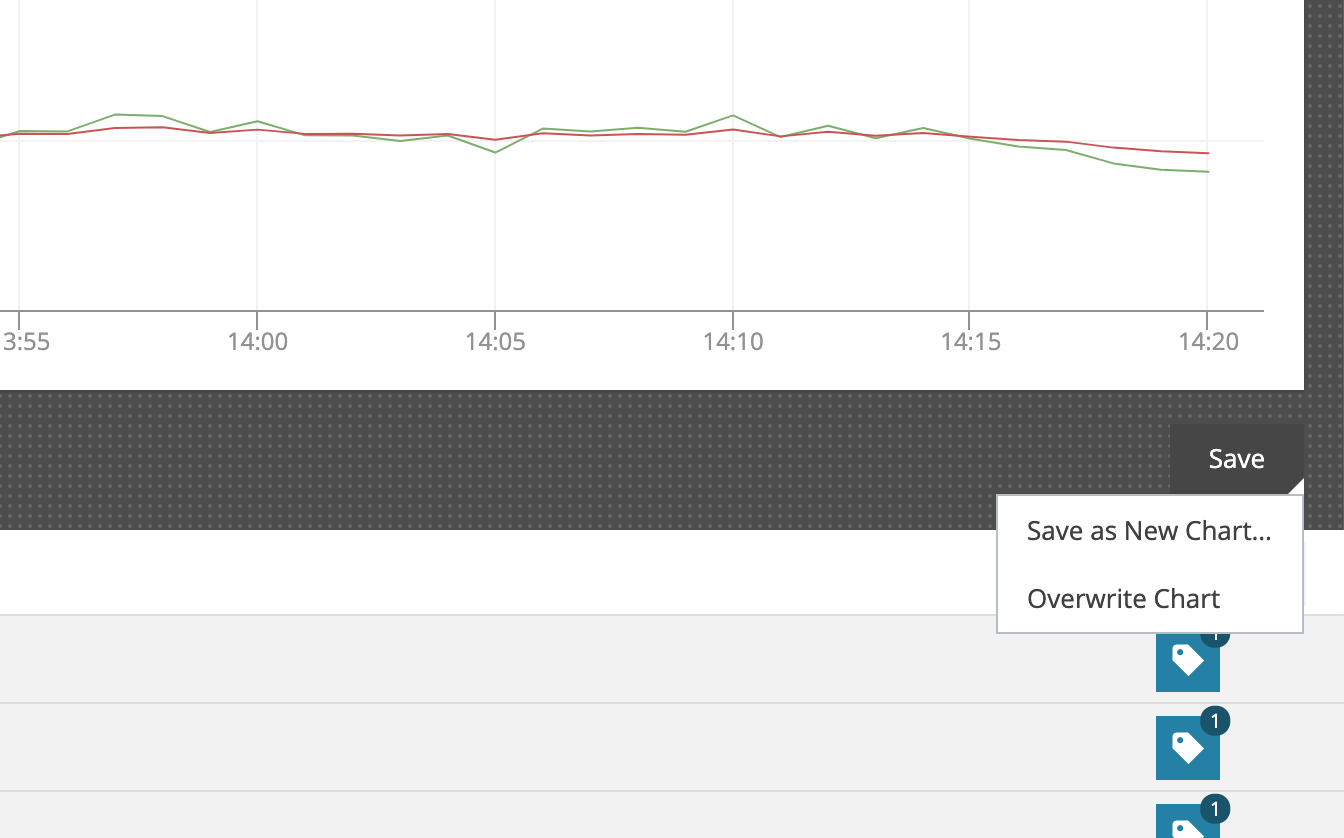
Chart Attributes & Log Y-Axis
The chart attributes allow you to set a title, a y-axis label, set the minimum and maximum values for the y-axis, and link the chart to another dashboard.
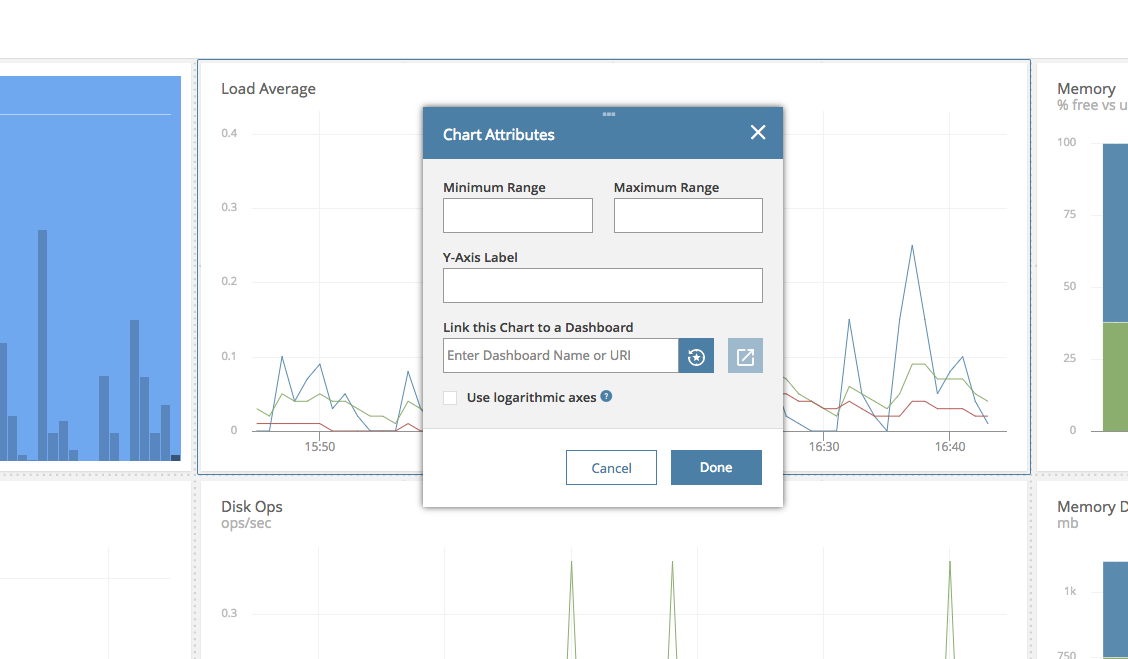
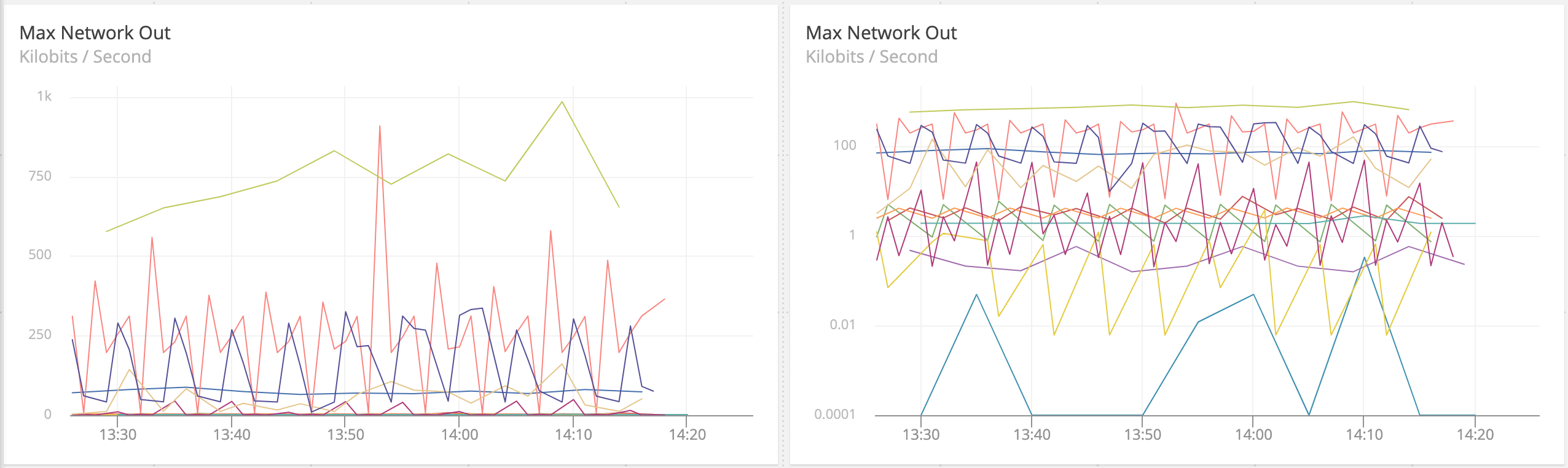
The chart attributes also provide the option to utilize a logarithmic scale instead of a linear scale. Logarithmic scales make it easy to compare values that cover a large range.
Snapshot
Create a permalink to an image of the chart or post it into your favorite chat agent. Read more in the Snapshots article.
Embed Chart
Read the embedding article to learn about embedding charts in your site or application.
Copy Chart
We've all been there: you have created a beautiful chart. It is awesome. Now you need to create another chart that is similar but not quite the same, so take advantage of Copy Charts which allows you to copy individual charts inside or across dashboards. This makes building similar charts much easier and makes transferring views across dashboards super convenient.
To get started, select copy from the menu of your chart:
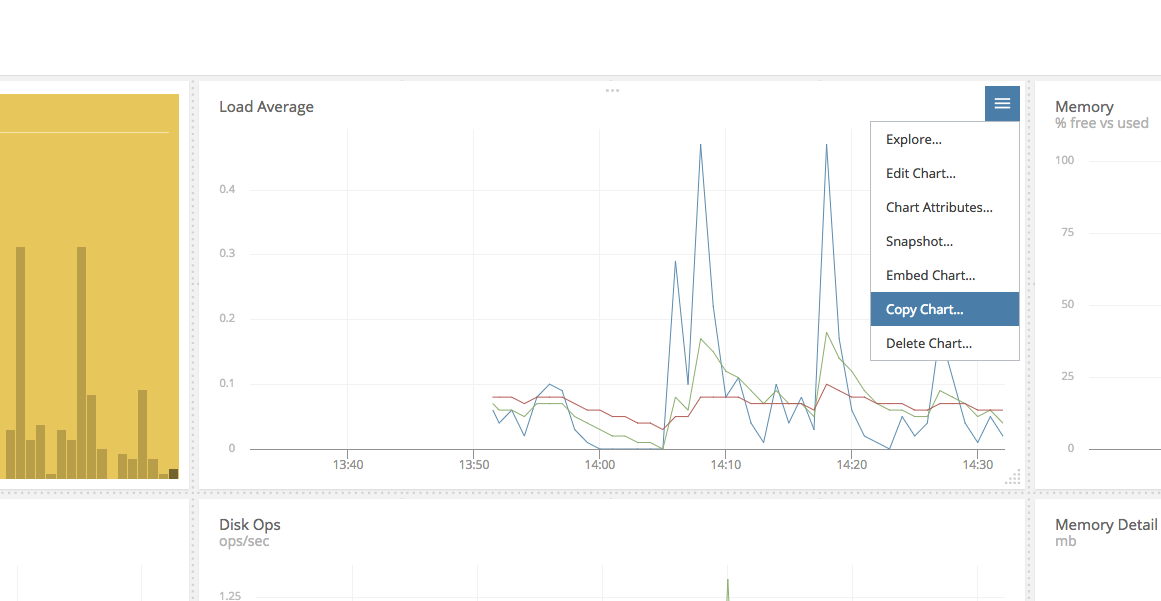
If you want, you can give the cloned chart a different name before copying. You may also copy charts to other dashboards.
Navigation Notice: When the APM Integrated Experience is enabled, AppOptics shares a common navigation and enhanced feature set with other integrated experience products. How you navigate AppOptics and access its features may vary from these instructions.
